서 론
비인두암은 비인두부의 상피에 발생하는 악성종양으 로 증상이 없거나 비출혈과 같은 비특이적 증상을 보여 늦게 발견하는 경우가 많아 예후가 좋지 않은 경향을 보 인다.1,2) 10만명당 15~30명의 발병률을 보이는 암으로 방 사선 치료에 비교적 잘 반응하기 때문에 주 치료로서 방 사선 단독요법 또는 항암방사선병합요법을 고려하게 된 다.3-6) 초기인 경우 방사선 치료 단독으로 완치가 가능한 데 이 경우 방사선 치료 후 5년 생존률은 85~90% 정도로 좋은 예후를 보이나 8~10% 정도에서는 재발을 경험하며 이들 중에는 원격전이가 발생하는 경우도 흔하다.5,6) 조 기 비인두암의 좋은 치료성적에 비하여 재발한 비인두 암의 경우 발견이 어렵고 진행된 병변으로 확인되는 경 우가 많아 좋지 않은 예후를 보인다.1,5,7) 재발한 비인두 암의 치료로는 방사선 치료의 재시도나 항암요법을 시 도해 볼 수 있으며 비인두부위에 병변이 국한되어 있는 조기 재발성 비인두암의 경우에는 수술적 절제를 제한 적으로 고려할 수 있다.4-6) 본 증례의 경우 정기적인 내시 경 검사를 통해 조기에 발견한 재발성 비인두암을 침습 적인 절개 또는 방사선치료의 재시도 없이 경비강 내시 경으로 제거하여 좋은 결과를 얻어 보고 하고자 한다.
증 례
59세 남자가 간헐적 비출혈을 주소로 본원 외래로 내 원하였다. 과거력 상 고혈압, 신증후군이 있었다. 음주력 은 주 1회 맥주1병 정도였고, 15갑년의 흡연력 있었다. 비인두내시경에서 좌측 비인두부에 경계가 불분명한 병 변이 관찰되었고(Fig. 1A), 종괴는 비인두강내 국한되어 있었다. 경부 이학적 검사상 구인두 및 비강에 특이소견 은 없었고, 경부 촉진에서도 종물은 만져지지 않았다. 경 부 전산화단층촬영에서 좌측 귀인두관 융기 내측에 0.6 × 0.6 cm 크기의 조영증강되는 종물이 관찰되었으며 (Fig. 1B), 경부 림프절 전이는 관찰되지 않았다. 펀치 생 검을 통한 조직검사 결과는 비각화 편평상피암종으로 비인두 암(T1N0M0, stage I)으로 진단하였다. 초 치료로 방사선 치료가 6840 cGy(38회) 시행되었다.
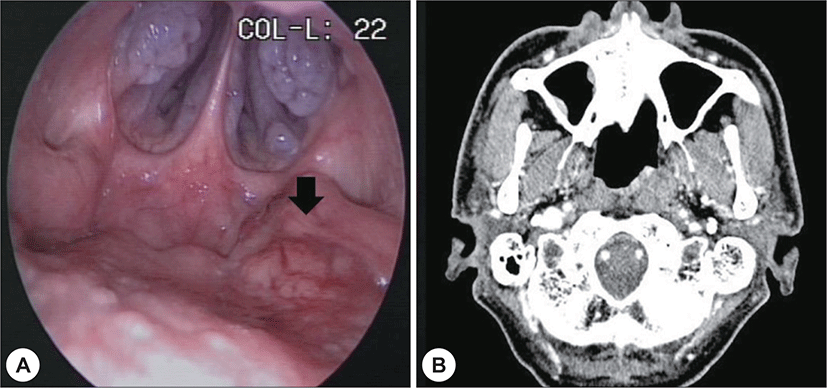
치료 21개월 후 비인두강 내시경상 좌측 비인두부에 경계가 불분명한 병변이 관찰되었고(Fig. 2A) 종양의 조 직검사 결과 저분화성 비각화 편평상피암종으로 확인되 어 재발성 비인두암으로 진단하였다. EBV면역조직검사 에서는 음성으로 확인되었다. 병기확인을 위한 PET 전 산화 단층촬영에서는 저명한 병변이 확인되지 않았고 경부 림프절이나 타 장기로의 전이 소견 또한 관찰되지 않았다.
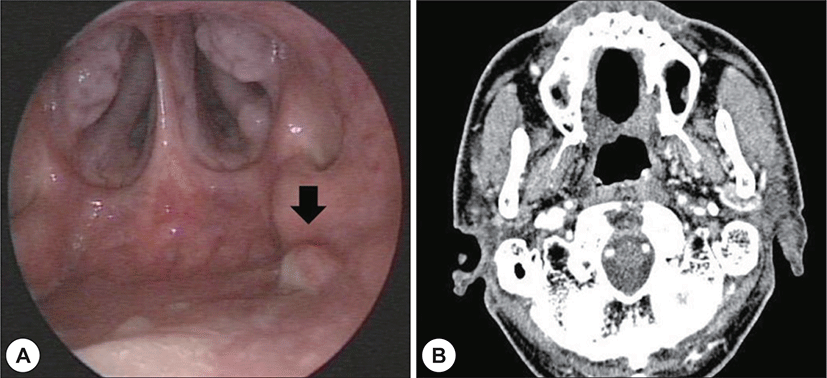
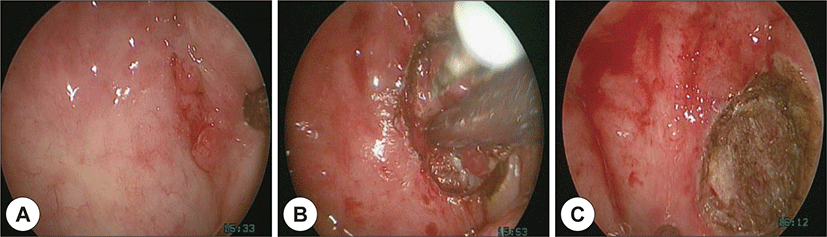
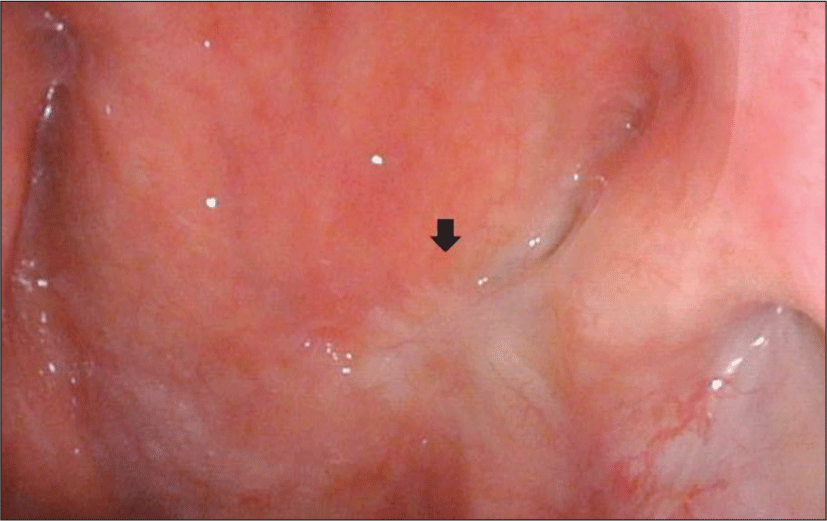
경부 전산화 단층촬영 영상에서 병변이 비교적 국한되 어 있고 점막 하로 깊이 침윤하는 소견이 관찰되지 않아, 경비강 내시경 수술을 시행하기로 하였다(Fig. 2B). 충분 한 수술 공간을 확보하기 위하여 양측 하비갑개 외향골 절술을 시행 하였으며 수술 기구의 충분한 가동범위를 확보하기 위하여 보조의가 우측 비강으로 내시경을 삽 입하여 좌측 비인두의 병변부위를 확인하였으며(Fig. 3A) 시야를 충분히 확보한 상태에서 좌측 비강으로 흡 입기나 내시경 겸자를 삽입하여 병변부위의 조직을 견 인하면서 우측 비강으로 삽입한 단극성 소작기를 이용 하여 병변의 절제범위를 표시하였다(Fig. 3B). 안전연은 0.5 cm으로 설정하였으며 단극성 소작기를 이용하여 상 인두수축근까지 안전변연을 확보하여 충분한 깊이로 병 변부위를 제거하였고(Fig. 3C) 1.6×1.6×2.0 cm 크기의 조직을 절제하였다. 이후 출혈부위를 양극성 소작기를 이용하여 지혈 후 수술을 마쳤으며 환자는 수술 1일째 특 별한 합병증 없이 퇴원하였다. 조직검사결과 0.6×0.8 cm 크기의 편평상피세포암으로 확인되었으며 절제변연은 음성으로 확인되었고 환자는 수술 2년 후 비인두내시경 및 영상학적 검사에서 암의 재발 없이 경과관찰 중이다 (Fig. 4).
고 찰
비인두암의 치료 방법은 병기에 따라 결정하는데, 방 사선 치료의 효과가 좋은 암종이므로 조기암의 경우 방 사선치료를 주로 시행하며 진행암의 경우 항암방사선병 합요법을 시행한다.5) 원발암의 수술적 절제는 재발암인 경우에 제한적으로 고려하게 된다.5,8) T1~2의 조기 비인 두암은 방사선 단독치료에 대한 국소반응률이 양호한 질 환이나 8~10.9% 정도에서 재발하게 되는데 재발한 비인 두암은 방사선치료에 저항성을 가질 수 있어 치료방법 의 선택이 제한적이며 50% 이상에서 진행된 병기로 발 견되기 때문에 좋지 않은 예후를 보일 수 있어 재발을 조 기에 발견하는 것이 중요하다.3,5-7,9)
일반적으로 방사선 치료에 대한 반응이 없는 경우 수 술적 절제를 고려해 볼 수 있으며, 전통적인 수술방법으 로 경상악 접근법과 경구개접근법, 경하악-익상접근법 이 있다.4,5,10) 이러한 수술은 비인두부로 접근을 위한 침습 적인 수술로 익상근의 손상 등의 이차적 손상으로 인한 개 구장애 및 삼킴장애와 안면변형 등의 가능성이 있다.4,10)
침습적인 수술적 치료에 비하여 경비강 내시경적 비인 두절제술은 조기 병변이나 국소 재발한 비인두암에서 시 행할 수 있는 최소 침습적인 수술적 접근법으로 좁은 비 강으로 인하여 구획 내 절제가 쉽지 않으며 비인두부의 괴사나 출혈, 과대비성과 같은 합병증이 발생할 수 있다 는 단점이 있으나 경상악 접근법 등의 침습적 접근법 보 다 시야확보에 용이한 이점이 있다.3) 또한 수술적 합병증 이 비교적 적으며 조직의 손상을 줄일 수 있고 회복기간 이 더 빠르다는 장점이 있다.5,11-13) 그리고 전통적인 접근 법에 비하여 경동맥과 같은 주요 구조물의 노출을 최소 화 할 수 있어 심각한 합병증의 가능성을 줄일 수 있다.10) 경비강 내시경수술을 이용한 재발성 비인두암 치료 후 2년 생존률은 80~100%, 국소 재발률은 12%로 보고되고 있다.5,10-14)
하지만 국내에서 재발성 비인두암의 경비강 내시경적 절제에 대한 보고는 없다.
본 증례에서는 방사선 치료 후 정기적인 비인두내시 경 검사를 시행하여 재발성 비인두암의 조기발견이 가 능하였다.13) 경비강 내시경을 이용한 시야 확보 및 종양 의 구획 내 절제를 시행하였으며 특별한 수술 합병증 없 이 퇴원하였고 이후 2년의 추적관찰 동안 재발소견은 보 이지 않았다. 비인두암의 초 치료 후 내시경을 이용한 정 기적인 추적관찰로 재발암이 초기에 발견되면 경비강 내시경 수술을 통하여 비교적 간단하고 안전하게 병변 을 절제할 수 있으므로 이를 재발성 비인두암의 치료방 법으로 고려해 볼 수 있겠다.






