서론
미분화성 다형성 육종(undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma)은 주로 사지와 후복강에서 발생하는 육종으로, 두경부 영역에서의 미분화성 다형성 육종은 매우 드물게 발생하며 주로 비강과 부비동에 발생하게 된다.1,2) 구인두에 발생하는 미분화성 다형성 육종은 전체 두경부 영역의 미분화성 다형성 육종의 약 10%를 차지한다.2) 편도의 미분화성 다형성 육종은 아직 국내에 보고된 바가 없으며, 본 증례의 저자들은 한쪽 구개 편도 종괴의 절제 후 진단된 미분화성 다형성 육종 1예를 보고하고자 한다.
증례
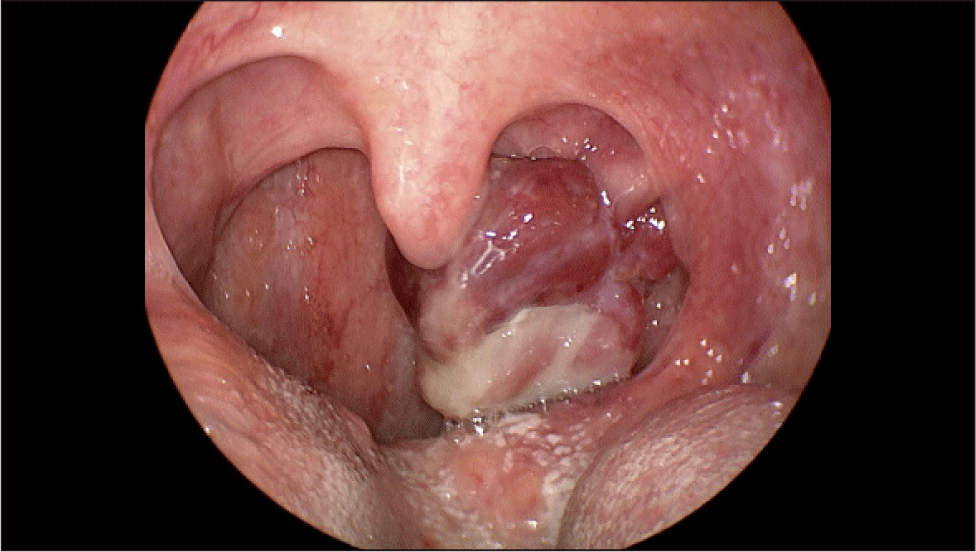
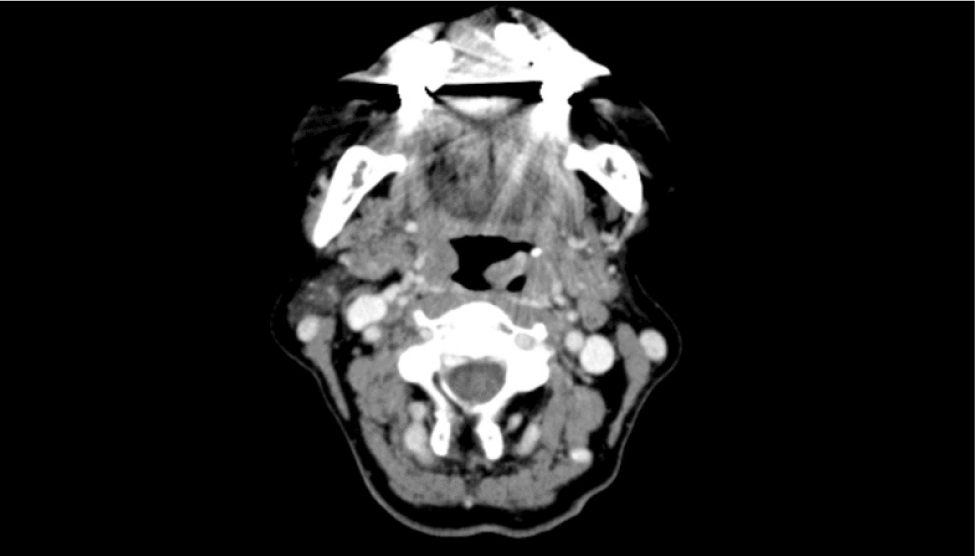
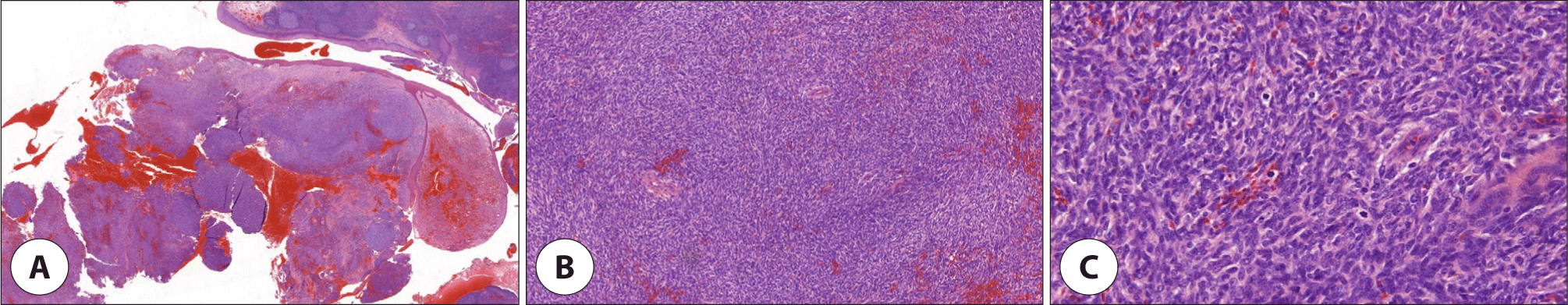
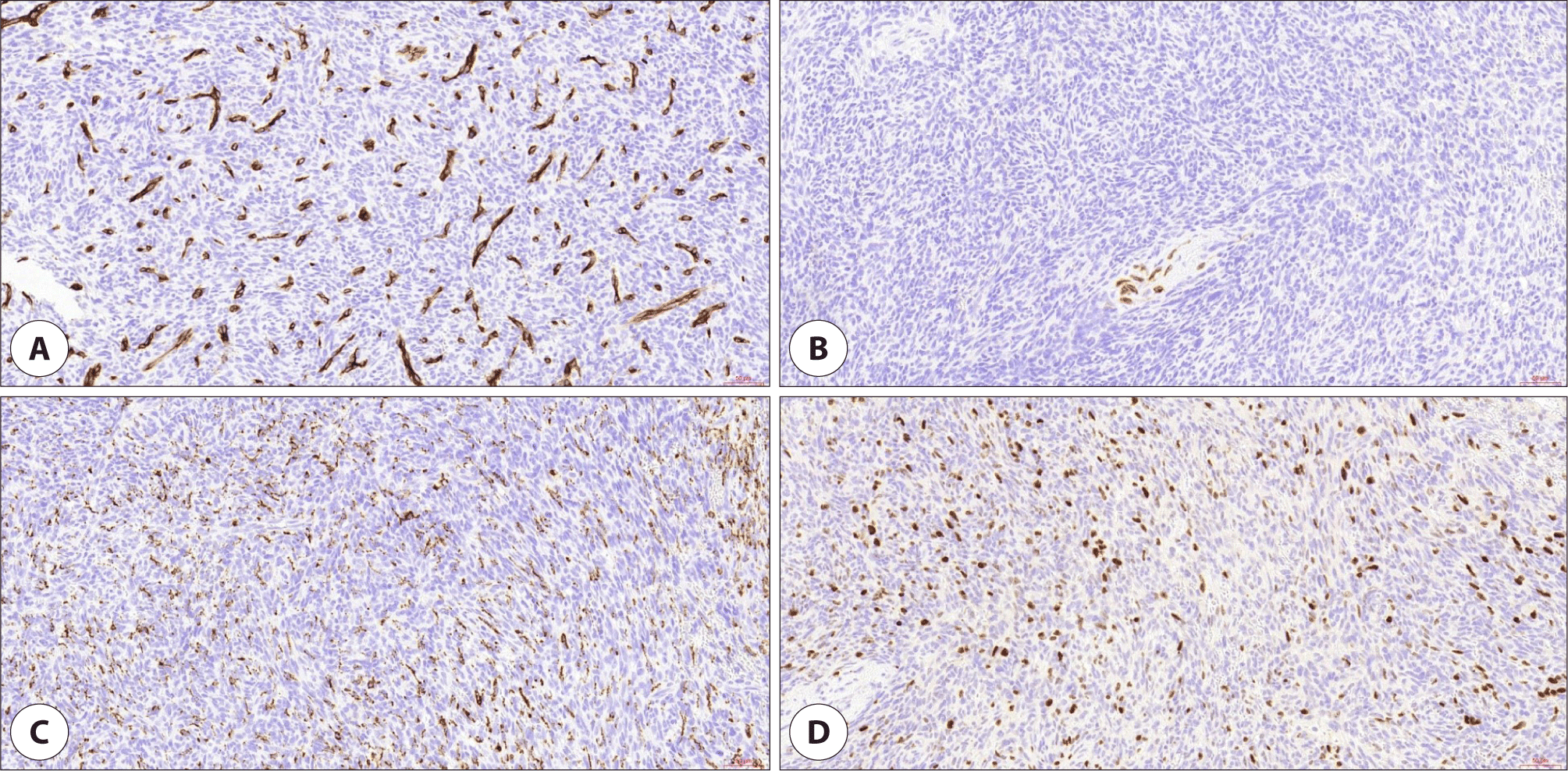
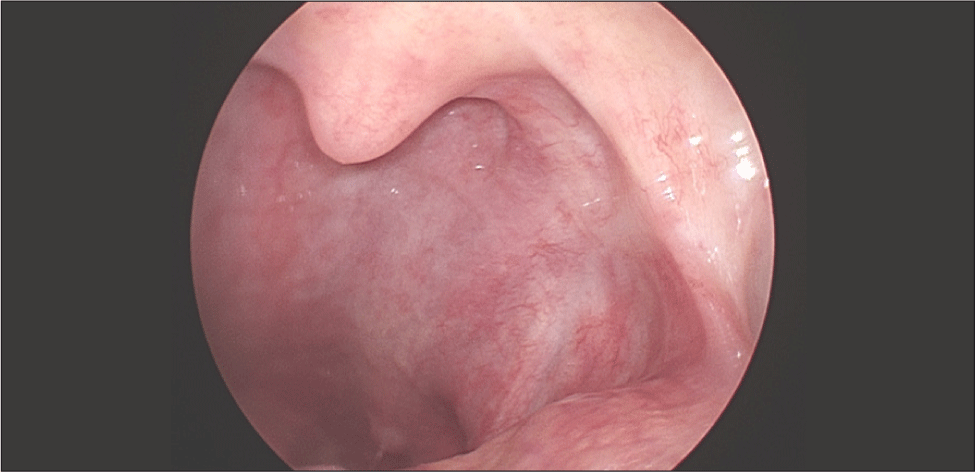
골다공증 외 별다른 기저질환 및 방사선 조사력이 없는 65세 여자 환자가 약 10일 전부터 발생한 목 안의 이물감으로 외래에 내원하였다. 환자는 종괴로 인한 목의 이물감뿐만 아니라 간헐적인 종괴에서의 출혈로 인한 불편감을 호소하였다. 후두경 상 좌측 구개편도에 유경성(pedunculated)의 종괴가 발견되었고, 종괴는 목젖을 넘어 비대하였지만 점막은 매끈하게 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 또한 경부 CT(computed tomography) 상에서는 좌측 구인두의 1.5 cm 크기의 조영 증강이 되는 유경성의 덩이가 관찰되었고, 경부 림프절에서의 유의미한 크기의 증가는 확인되지 않았다(Fig. 2). 본 증례의 저자들은 편도의 폴립이나 육아종 등의 양성종양을 의심하였으나, 종물의 크기가 커서 전신마취 후 완전 절제 수술을 시행하기로 하였다. 수술은 일반적으로 편도절제를 실시하는 과정과 유사하게 상인두수축근을 보존하며 진행하였고, 약 3.2×2.8×2.0 cm, 5 g의 구개편도 종괴를 적출하였다. 종괴는 정상 점막에 울퉁불퉁한 표면을 띠고 있었으며, 단면은 부드러운 황갈색을 띠고 있었다. 조직검사 상 저배율(1.4배)에서는 방추세포(spindle cell)로 구성된 결절의 증식이 관찰되었고(Fig. 3A), 10배율 시야에서 결절의 방추세포는 소용돌이(storiform) 모양과 작은 다발(fascicle) 모양으로 배열되어 있었으며, 조직의 전반적인 미세출혈과 10개 이상의 비정상적 유사 분열을 다량 관찰할 수 있었다(Fig. 3B). 40배율 시야에서도 마찬가지로 비정상적 유사분열을 명확하게 관찰할 수 있었다(Fig. 3C). 면역조직화학염색검사에서는 CD34, SMA, S-100, desmin 염색에서는 음성 반응을 보였으나(Fig. 4A, B), CD68, CD99에서 양성, Ki-67에서 2+ 양성 소견을 보였다(Fig. 4C, D). 최종적으로 미분화성 다형성 육종(undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma)이 진단되었고, 절제연에서 육종이 확인되었다. 수술 후 시행한 PET(positron emission tomography)-CT 상에서 경부 전이나 원격 전이 등 추가로 발견되는 이상소견은 없었다.
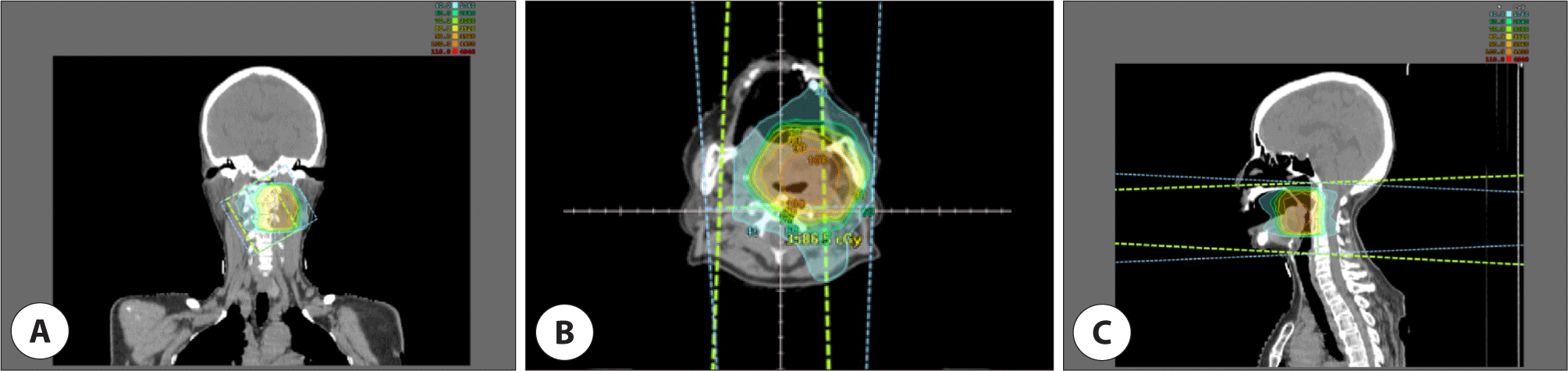
조직검사결과에서 절제연은 양성이었지만, 육안으로 확인되는 잔여 암종은 없는 것으로 판단되었고, 다학제 진료 후 추가적인 수술 없이 방사선치료를 하는 것으로 결정하였다. 수술 후 5주부터 30회에 걸쳐 총 60 Gy의 방사선을 수술 부위인 좌측 편도와 주변조직에 조사하였고 경부림프절은 포함하지 않았다(Fig. 5). 이후 국소 재발 및 원격 전이 등의 특이소견을 보이지 않은 채 4년째 외래를 통해 추적관찰 중이다(Fig. 6).
고찰
두경부 영역에서의 악성 종양은 주로 편평상피세포암이 대부분을 차지하며 육종 (sarcoma)의 발생은 상대적으로 매우 드물다. 두경부 영역의 종양 중 육종은 약 1% 미만을 차지하고 있으며, 전체 육종의 약 5%–20%가 두경부 영역에서 발생한다고 알려져 있다. 두경부 영역에서의 육종 중 횡문근육종(rhabdomyosarcoma)이 미분화성 다형성 육종과 함께 흔히 발생한다고 알려져 있으며, 그 외 혈관육종(angiosarcoma), 섬유육종(fibrosarcoma), 신경원성 육종(neurogenic sarcoma) 등이 발생할 수 있다.1)
미분화성 다형성 육종은 이전에 악성 섬유성 조직구종(malignant fibrous histiocytoma)이라고 불리운 종양이며, 이전에는 조직구(histiocyte)에서 기원한 악성종양으로 생각하였으나 현재는 중간엽 줄기세포(mesenchymal stem cell)에서 기원한 것으로 추정되어 육종의 명명이 변경되었다.3) 미분화성 다형성 육종은 주로 50대 이상의 고령에서, 남성에서 여성보다 약 1.8배 정도 발생률이 높으며 주로 하지, 상지 및 후복강(retroperitoneum) 영역에서 발생한다고 알려져 있다.4) 약 10% 미만의 미분화성 다형성 육종이 두경부 영역에서 발생하며, 전체 두경부 영역의 악성 종양 중 0.5%를 차지하는 아주 드문 종양이지만 연부 조직에서 기원하는 종양이기에 인후두 영역뿐만 아니라 두경부의 근육, 피부 등의 조직에서도 발생할 수 있다는 특징이 있다.5) 두경부 영역에서의 미분화성 다형성 육종의 약 30%가 비강과 부비동의 영역에서 발생하며, 그 외 두개안면골, 후두, 목의 연조직, 주타액선, 구강, 인두 및 안구 영역 순으로 잘 발생한다고 알려져 있다.2)
미분화성 다형성 육종은 통증을 동반하지 않고 수 개월에 걸쳐서, 단일성으로 크기가 커지는 양상을 보이며, 육안관찰 시 발생 초기에는 매끈한 표면을 띨 수 있으나 육종의 침범이 심화될수록 불규칙한 표면과 함께 출혈, 괴사 및 육종 부위의 괴사를 동반할 수 있다. 이와 더불어 미분화성 다형성 육종은 발생하는 위치에 따라 다양한 증상을 유발할 수 있다.5) 후두부 및 성문하 부위를 침범하는 경우, 쉰 목소리 및 호흡 시의 불편함을 유발할 수 있으며, 종양의 크기가 커지게 되면 심한 호흡곤란 및 협착음이 발생할 수 있다.6) 구인두를 침범하는 경우 본 증례에서와 같이 목의 이물감을 호소할 수 있으며, 심할 경우 삼킴곤란 및 삼킴통증을 일으킬 수 있다.7) 비강을 침범하는 경우에는 코막힘, 비출혈, 비강 영역의 감각저하를 일으킬 수 있으며 종양의 비대로 인하여 시신경이 압박되는 경우 시야 및 시력에 영향을 미칠 수도 있다.8)
미분화성 다형성 육종은 조직검사를 통해 확진할 수 있다. 두경부 영역의 미분화성 다형성 육종의 검체 채취를 위하여 중심침생검 검사 또는 절개 생검이 선호되며, 세침 흡인검사는 조직을 채취에 용이하지 않아 선호되지 않는다. 육안상으로는 경계가 비교적 뚜렷한 종괴 형태를 띠며 막으로 둘러싸여 있지 않고, 단면은 회백색을 띠나 염증이나 괴사가 동반된 경우 노란색을 띨 수 있다. 현미경검사 상에서는 조직에서의 비전형적인, 다형성의 방추세포(spindle cell)가 다량 관찰되며 방추세포들은 혈관 주변으로 소용돌이(storiform) 모양으로 배열되어 있는 것을 관찰할 수 있다. 또한 비전형적인 유사분열상이 전형적인 유사분열상과 함께 광범위하게 관찰되며 간헐적으로 호산구성의 세포질의 다핵거대세포가 관찰될 수 있다.9) 최종 조직확진을 위하여 면역조직화학염색검사를 통해 다른 육종을 배제하는 것이 필요한데, keratin, S-100 단백질, SOX10, SMA, desmin에 음성을 보이면 미분화성 다형성 육종으로 진단을 할 수 있다.10) Vimentin, CD68, CD99, Lysozyme, Ki-67, EGFR, COX-2 및 p53 염색에 양성 반응을 보이나, 진단에 비특이적이고 간헐적으로 염색에 음성을 보이기도 한다.11) 본 증례에서는 CD68, CD99와 Ki-67 염색에서 양성 소견을 보였다.
영상학적 검사만으로는 두경부 영역의 미분화성 다형성 육종을 진단할 수 없지만, 크기, 위치 및 주위 구조물과의 위치관계를 통하여 육종의 병기를 설정하고 치료 계획을 수립하는 있어 많은 도움을 줄 수 있다.2) 전산화단층촬영에서는 주위 근육조직과 비슷한 밀도를 띠며 자기공명영상에서는 T1 강조영상에서 저신호에서 중등도 신호강도, T2 강조영상에서는 중등도 신호강도에서 고신호강도 소견을 보인다. 전산화단층촬영영상 및 자기공명영상에서 육종 내부의 출혈이나 괴사, 석회화 정도에 따라 불균일성이 달라질 수 있고, 또한 자기공명영상의 T1 강조영상에서 조영제를 사용하였을 시 조영증강이 잘 되는 모습을 관찰할 수 있다.2)
두경부 영역에서의 미분화성 다형성 육종은 충분한 절제면을 둔 수술적 완전 절제를 원칙으로 하며 수술 후 조직검사 결과에 따라 방사선 치료를 추가로 진행할 수 있다. 문헌에 따르면 조직학적으로 고등급의 종양일 경우, 육종의 절제면이 양성일 경우, 육종의 크기가 5 cm 이상일 경우, 재발성 육종일 경우 수술 후 방사선 치료를 추가로 진행하는 것을 권장하며, 방사선 치료를 추가로 진행한 경우 수술적 치료만 진행하였을 경우와 비교하여 통계적으로 유의미하게 재발율과 생존율에 차이가 있었다.12,13)
두경부 영역의 미분화성 다형성 육종의 5년 생존율은 사지의 미분화성 다형성 육종의 그것보다 좋지 않은 것으로 알려져 있다. Sabesan의 연구에 의하면 두경부 영역과 사지 영역의 미분화성 다형성 육종 환자의 5년 생존율은 각각 약 48%와 77%로 유의미한 차이가 있었다.14) 이는 사지에 비한 두경부 영역에서의 구조물이 복잡성으로 인해 수술 시 절제면을 충분히 확보하지 못할 수 있다는 점과, 사지 영역에 비해 상대적으로 드물게 발생한다는 점이 두 영역의 생존율의 차이를 발생시켰을 가능성이 있다. 또한 국소 재발율에 있어서는 두경부 영역과 사지 영역의 유의미한 차이는 관찰되지 않았으나, 절제면이 충분히 확보되면 확보될수록 국소 재발율의 유의미한 감소를 보여 수술 시 충분한 절제면을 확보하는 것이 중요할 것으로 사료된다.
일반적으로 편도의 악성종양은 경돌인두근, 경돌설근 등을 포함하여 종양을 절제하는 경구강 측부 구인두절제술(transoral lateral oropharyngectomy) 또는 구강 로봇수술 등의 술식으로 제거하나, 본 증례에서는 양성종양으로 생각하고 조직검사를 시행하지 않았기 때문에 단순 편도절제에 준해 수술을 진행하였다. 65세의 성인에서 한쪽 구개편도에만 발생한 종괴이므로 악성종양의 가능성을 완전 배제하지 않고 수술전 조직검사를 시행하였다면 수술 시 좀 더 광범위한 절제연을 포함한 절제수술을 시행할 수 있었을 것으로 사료된다. 편도 및 구인두에서 발생한 미분화성 다형성 육종은 비교적 드문 증례임과 더불어, 본 사례와 같이 종양의 비교적 매끈한 표면으로 인하여 육아종, 섬유종 등 양성 종양으로 생각되는 종괴에서도 악성종양의 가능성을 완전히 배제하지 않고 미분화성 다형성 육종이 감별진단에 포함되어야 할 것으로 생각되어 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하는 바이다.
